
The Project Explorer displays a hierarchical list of all the Groups, forms and controls you have added to your project. When you select an element in the Project Explorer, corresponding information about the selection is displayed in the main program window.
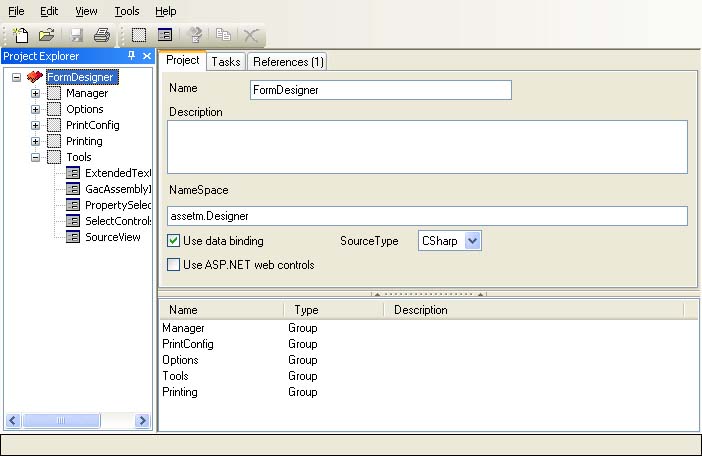
Selecting the project itself at the root of the Project Explorer (as shown above) allows you to set global project preferences such as the target programming language — currently VB.NET and C# are supported — or the namespace that should be added to the generated code.
 If you start with an empty project, you can add new items to it by right-clicking on the project name in the Project Explorer and selecting either "Add Group" or "Add Rootform".
If you start with an empty project, you can add new items to it by right-clicking on the project name in the Project Explorer and selecting either "Add Group" or "Add Rootform".
A Rootform can be a .NET Windows Form or a UserControl, depending on how you configure it using the "Formtype" dropdown list (see below).
A Group is a logical container for Rootforms that provides you with both a means of structuring your project within form.suite4.net and within the generated code because Group names are included as namespaces in the code generation output.
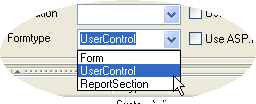 After you selected a form in the Project Explorer, you can view and edit its properties in the main program window. If you want to turn a form into a user control (or vice versa) simply select the desired type from the "Formtype" dropdown list.
After you selected a form in the Project Explorer, you can view and edit its properties in the main program window. If you want to turn a form into a user control (or vice versa) simply select the desired type from the "Formtype" dropdown list.
Tasks can be assigned to individual forms or controls, to groups and the project itself. Linking tasks to controls is done in the Form Designer as described in Task/Description Board. To add tasks to a project or group complete the following steps:
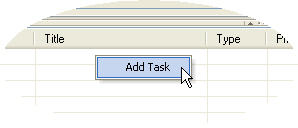 Right-click on the list in the bottom half of the window and select "Add task" from the context menu. A new task is added to the list.
Right-click on the list in the bottom half of the window and select "Add task" from the context menu. A new task is added to the list. 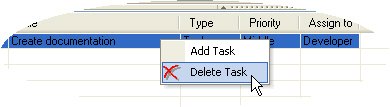 Select the task that is to be deleted.
Select the task that is to be deleted.form.suite4.net can convert forms and controls of a project to ASP.NET web forms and user controls. A number of settings in the Form Manager determine the parameters of the conversion.
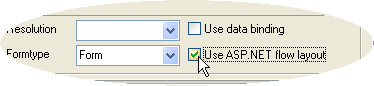 "Use ASP.NET flow layout". This setting is available from the details pane after you selected a form or control in the Project Explorer. It determines the method employed to place controls onto the ASP.NET page or user control when the selected form is converted to ASP.NET.
"Use ASP.NET flow layout". This setting is available from the details pane after you selected a form or control in the Project Explorer. It determines the method employed to place controls onto the ASP.NET page or user control when the selected form is converted to ASP.NET. <asp:TextBox id="MyTextBox" runat="Server" style="position:absolute;top:15px;left:25px; [...]">[...]</asp:TextBox>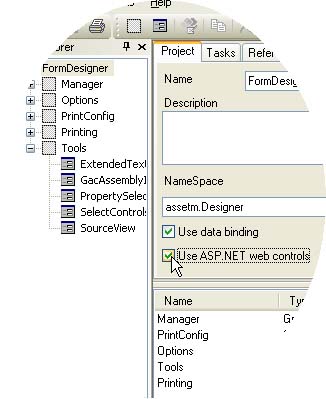 "Use ASP.NET Web controls". This project-wide setting refers to the way layout tables for holding the controls are being generated when using Flow Layout (see above).
"Use ASP.NET Web controls". This project-wide setting refers to the way layout tables for holding the controls are being generated when using Flow Layout (see above).
<asp:Table id="Table1" runat="Server">
<asp:TableRow runat="Server">
<asp:TableCell runat="Server">[...]</asp:TableCell>
</asp:TableRow>
<asp:Table>
<table [...]>
<tr>
<td>[...]</td>
</tr>
</table>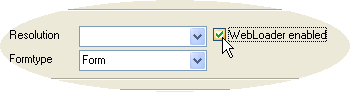 The WebLoader component
is unique feature of form.suite4.net that
allows you to publish an existing form on a web page. Activating the "WebLoader
enabled" checkbox does just that -- it enables a form or control you selected
in the Project Explorer to be used in conjunction with the WebLoader component.
After you activated the checkbox, an additional panel appears in the Form
Designer that allows you to configure
the WebLoader interaction.
The WebLoader component
is unique feature of form.suite4.net that
allows you to publish an existing form on a web page. Activating the "WebLoader
enabled" checkbox does just that -- it enables a form or control you selected
in the Project Explorer to be used in conjunction with the WebLoader component.
After you activated the checkbox, an additional panel appears in the Form
Designer that allows you to configure
the WebLoader interaction.